Advanced high-strength steel (AHSS) 690 Grade refers to a type of steel with a high yield strength of approximately 690 MPa, known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and suitability for demanding applications in automotive, aerospace, and structural engineering. Laser welding, a precise and efficient welding technique, is increasingly used to join AHSS 690 due to its specific advantages and challenges:
PEAKKONG Special Steel’s high-power automated welding, 20mm without bevel, direct penetration, maximum welding thickness 60mm.
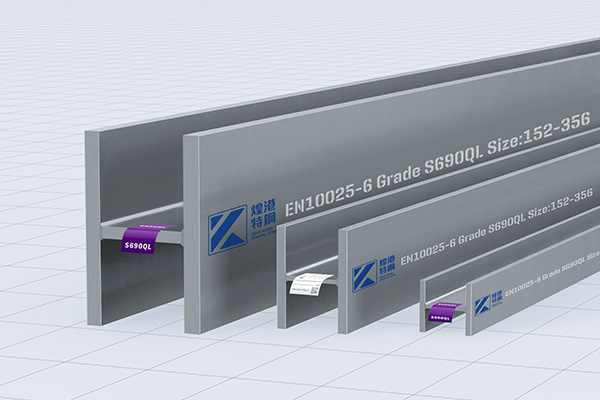
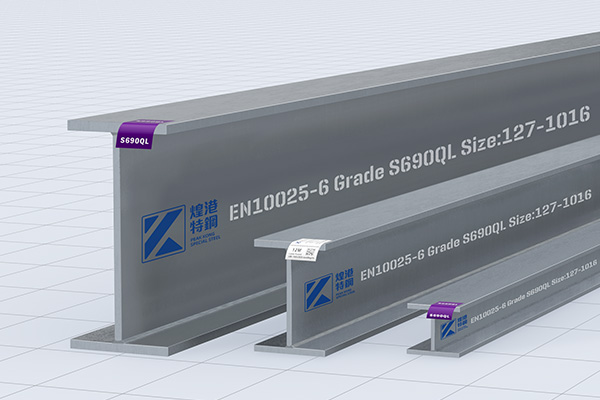
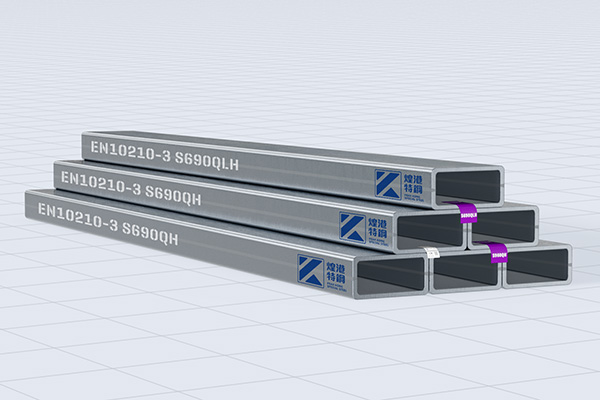
PEAKKONG Special Steel has launched S690 I-beams, H-beams, channels, angles, square tubes, flat tubes, round tubes.
High Welding Speed: Laser welding is capable of high welding speeds, contributing to increased productivity in manufacturing.
Precision and Control: Laser welding offers precise control over heat input, minimizing distortion and preserving the mechanical properties of AHSS 690 Grade.
Narrow Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ): Laser welding produces a small HAZ, reducing the risk of softening or weakening the surrounding material.
Versatility: Laser welding can accommodate various joint designs and thicknesses of AHSS 690 Grade, providing flexibility in design and manufacturing.
Clean and Aesthetic Welds: Laser welding typically results in clean, aesthetically pleasing welds with minimal spatter, reducing the need for post-weld cleanup.
Material Sensitivity: AHSS 690 Grade is sensitive to heat input during welding, which can affect its microstructure and mechanical properties if not controlled properly.
Joint Design: Designing suitable joint configurations and preparing the material surfaces are crucial for achieving strong welds in AHSS 690 Grade.
Process Optimization: Parameters such as laser power, welding speed, beam focus, and shielding gas must be carefully optimized to ensure consistent weld quality and performance.
Weld Integrity: Ensuring the integrity of the weld, including avoiding defects such as porosity and cracks, requires thorough process control and monitoring.
Post-Weld Treatment: Depending on the application, some laser-welded joints in AHSS 690 Grade may require additional treatment to achieve desired mechanical properties and corrosion resistance.
Laser welding of AHSS 690 Grade is commonly employed in industries such as automotive manufacturing (for chassis, safety components), aerospace (structural elements), and structural engineering (bridges, high-rise buildings) where high strength and lightweight construction are paramount.
In conclusion, laser welding is a powerful method for joining AHSS 690, offering advantages in speed, precision, and control while requiring careful consideration of material properties and process parameters to ensure optimal weld quality and performance.
-
 2024-9-20 Application of Ti Gr 7/3.7235/UNS R52400 Structural Hollow Stations
2024-9-20 Application of Ti Gr 7/3.7235/UNS R52400 Structural Hollow Stations -
 2024-9-29 Alloy 2.4663 (N06617 / Alloy 617) Structural Hollow Profiles
2024-9-29 Alloy 2.4663 (N06617 / Alloy 617) Structural Hollow Profiles -
2024-9-27 926 / 1.4529 stainless steel structural hollow sections
-
 2024-9-25 1.4547 Super Stainless Steel for Structural Applications
2024-9-25 1.4547 Super Stainless Steel for Structural Applications -
 2024-6-22 Innovative application of high-strength steel structural Sections
2024-6-22 Innovative application of high-strength steel structural Sections -
 2024-9-21 S960QH/S960QLH Hollow structural Stations in Hong Kong
2024-9-21 S960QH/S960QLH Hollow structural Stations in Hong Kong -
 2024-4-15 Duplex Stainless Steel – A Simple Guide
2024-4-15 Duplex Stainless Steel – A Simple Guide